Groups & Clusters of Galaxies
Feasting Black Holes Caught in Galactic Spiderweb

Spiderweb Galaxy Field
Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/INAF/P. Tozzi et al; Optical (Subaru): NAOJ/NINS; Optical (HST): NASA/STScI
Often, a spiderweb conjures the idea of captured prey soon to be consumed by a waiting predator. In the case of the "Spiderweb" protocluster, however, objects that lie within a giant cosmic web are feasting and growing, according to data from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory.
The Spiderweb galaxy, officially known as J1140-2629, gets its nickname from its web-like appearance in some optical light images. This likeness can be seen in the inset box where data from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope shows galaxies in orange, white, and blue, and data from Chandra is in purple. Located about 10.6 billion light years from Earth, the Spiderweb galaxy is at the center of a protocluster, a growing collection of galaxies and gas that will eventually evolve into a galaxy cluster.
An Expanse of Light

An Expanse of Light
Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/SAO; Optical: NASA/STScI, Palomar Observatory, DSS;
Radio: NSF/NRAO/VLA; H-Alpha: LCO/IMACS/MMTF
The recent launches of the James Webb Space Telescope (Webb) and the Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE) by NASA and its international partners are excellent reminders that the universe emits light or energy in many different forms. To fully investigate cosmic objects and phenomena, scientists need telescopes that can detect light across what is known as the electromagnetic spectrum.
This gallery provides examples of the ways that different types of light from telescopes on the ground and in space can be combined. The common thread in each of these selections is data from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory, illustrating how X-rays — which are emitted by very hot and energetic processes — are found throughout the Universe.
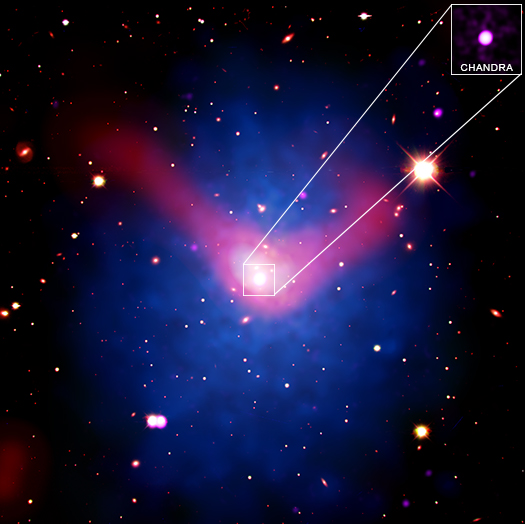
"Mini" Monster Black Hole Could Hold Clues to Giant's Growth
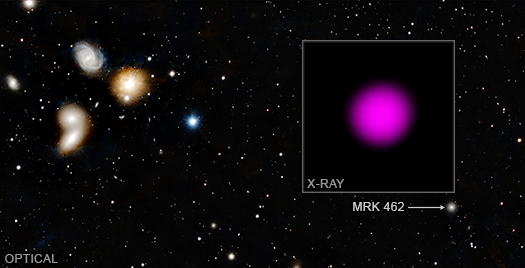
The graphic shows X-rays that NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory detected from the dwarf galaxy Mrk 462. This X-ray emission (inset) is important because it reveals the presence of a growing supermassive black hole within this relatively small galaxy, as described in our latest press release. The mass contained in this black hole — about 200,000 times the mass of the Sun — provides information to astronomers about how some of the earliest black holes in the Universe may have formed and grown billions of years ago.
The background panel is an optical image from the Pan-STARRS telescope in Hawaii. There are several galaxies that are part of the HCG068 galaxy group on the left-hand side of the image. The galaxy that is emitting copious amounts of X-rays, however, is the much smaller galaxy located to the lower right of the image (marked by the arrow). Mrk 462 is a dwarf galaxy because it contains only a few hundred million stars, which means it holds about a hundred times fewer stars than a galaxy like the Milky Way. Black holes are notoriously hard to find in dwarf galaxies because they are usually too small and dim for optical light telescopes to track the rapid motions of stars in the centers.
Astronomers Spy Quartet of Cavities From Giant Black Holes
Galaxy Cluster RBS 797
Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/Univ. of Bologna/F. Ubertosi; Optical: NASA/STScl/M.Calzadilla
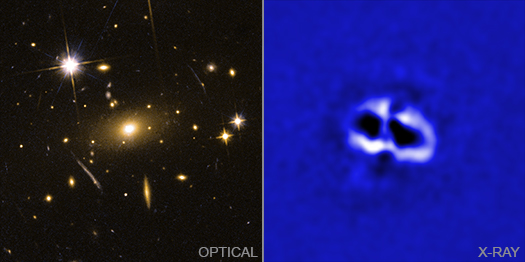
Four enormous cavities, or bubbles, have been found at the center of a galaxy cluster using NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory, as described in our latest press release. The left panel of this graphic shows an optical image of the galaxy cluster called RBS 797, from NASA's Hubble Space Telescope. Hot gas that envelopes the individual galaxies is invisible in optical light, but it is detected in X-rays by Chandra (right). One pair of cavities can be seen towards the left and right of center in the Chandra image as black oval-shaped regions. The other pair is less distinct, but can be found above and below the center of the image.
Chandra Catches Slingshot During Collision
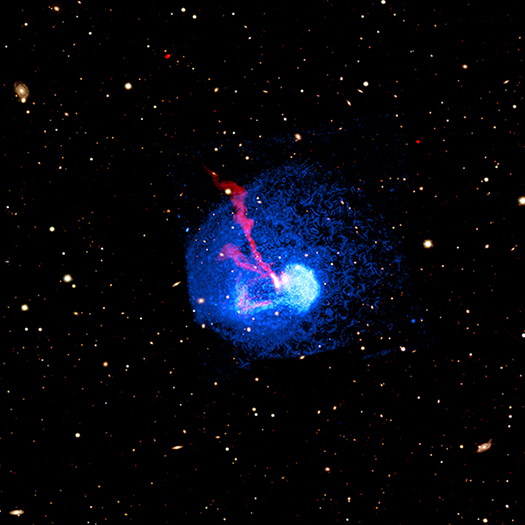

Abell 1775
Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/Leiden Univ./A. Botteon et al.; Radio: LOFAR/ASTRON; Optical/IR:PanSTARRS
When the titans of space — galaxy clusters — collide, extraordinary things can happen. A new study using NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory examines the repercussions after two galaxy clusters clashed.
Galaxy clusters are the largest structures in the Universe held together by gravity, containing hundreds or even thousands of individual galaxies immersed in giant oceans of superheated gas. In galaxy clusters, the normal matter — like the atoms that make up the stars, planets, and everything on Earth — is primarily in the form of hot gas and stars. The mass of the hot gas between the galaxies is far greater than the mass of the stars in all of the galaxies. This normal matter is bound in the cluster by the gravity of an even greater mass of dark matter.
Because of the huge masses and speeds involved, collisions and mergers between galaxy clusters are among the most energetic events in the universe.
In a new study of the galaxy cluster Abell 1775, located about 960 million light years from Earth, a team of astronomers led by Andrea Botteon from Leiden University in the Netherlands announced that they found a spiral-shaped pattern in Chandra's X-ray data. These results imply a turbulent past for the cluster.
Galaxy Cluster Travels Down an Intergalactic Highway

The Northern Clump
Credit: X-ray: (Chandra: NASA/CXC/Univ. Bonn/A. Veronica et al; XMM-Newton: ESA/XMM-Newton); Optical: DES/DOE/FNAL/DECam/CTIO/NOIRLab/NSF/AURA; Radio: CSIRO/ASKAP/EMU
Researchers have found a galaxy cluster acting like a passenger on what astronomers are calling an "intergalactic highway." The cluster is known as the "Northern Clump" and it is located about 690 million light years from Earth. Previously, scientists discovered an enormous filament, a thin strip of very hot gas that stretched for at least 50 million light years. A new study found evidence that the Northern Clump is traveling along this filament, similar to how a car moves along the interstate.
Three's a Crowd: Triple Galaxy Collisions and Their Impact on Black Hole Accretion

Adi Foord
We are pleased to welcome Adi Foord as a guest blogger. Adi is the first author of a pair of papers that are the subject of the latest Chandra press release. She is a Post postdoctoral fellow at the Kavli Institute of Particle Astrophysics and Cosmology at Stanford University. She received her bachelor's degree in Physics & Astronomy from Boston University in 2014, and recently received her Ph.D. in Astronomy & Astrophysics from the University of Michigan (Summer 2020). Adi is a high-energy astrophysicist who is interested in how and which environmental properties impact supermassive black hole accretion and evolution. Most of her work uses X-ray observations of supermassive black holes, and she is currently focusing on systems where two supermassive black holes are in the process of merging.
With the advancement of gravitational wave detectors such as LIGO, we are starting to get real proof that black holes exist, and that some evolve over time via mergers with other black holes. The black holes that gravitational wave detectors like LIGO study are solar mass black holes. As the name and unit imply, these black holes have masses between about five and 100 times that of the sun, and are believed to be formed after the death of a massive star. But what about supermassive black holes, the massive counterparts to solar mass black holes that lie at the center of most massive galaxies? With the groundbreaking image supplied by the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) in April 2019, we were given proof that supermassive black holes exist as well. But in order to have proof that they merge, and emit gravitational waves, we will have to wait for results from pulsar timing arrays (PTAs) and space-based interferometry (such as LISA). This is because the expected gravitational wave frequencies the supermassive black hole mergers are theorized to emit are outside the range of LIGO.
On the Hunt for a Missing Giant Black Hole
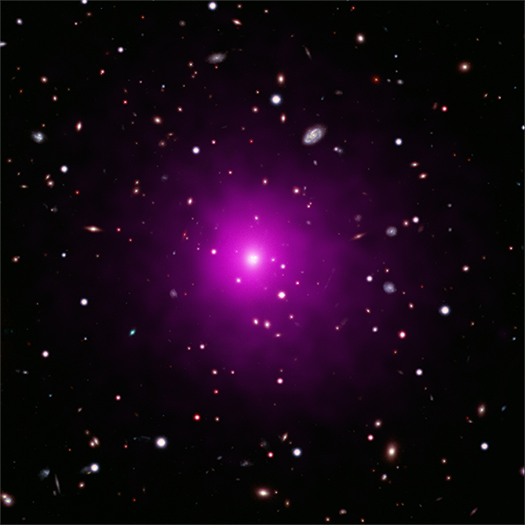

Abell 2261
Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/Univ of Michigan/K. Gültekin;
Optical: NASA/STScI and NAOJ/Subaru; Infrared: NSF/NOAO/KPNO
The mystery surrounding the whereabouts of a supermassive black hole has deepened.
Despite searching with NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory and Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers have no evidence that a distant black hole estimated to weigh between 3 billion and 100 billion times the mass of the Sun is anywhere to be found.
This missing black hole should be in the enormous galaxy in the center of the galaxy cluster Abell 2261, which is located about 2.7 billion light years from Earth. This composite image of Abell 2261 contains optical data from Hubble and the Subaru Telescope showing galaxies in the cluster and in the background, and Chandra X-ray data showing hot gas (colored pink) pervading the cluster. The middle of the image shows the large elliptical galaxy in the center of the cluster.
History of SpARCS1049

Carter Rhea
We welcome Carter Rhea as our guest blogger and a co-author of a paper that is the subject of our latest press release. Carter completed his undergraduate degree in astronomy at the College of Charleston in Charleston South Carolina. Afterwards, he obtained a master’s degree in scientific computing and computational mechanics at Duke University. Instead of continuing with a PhD, he decided to return to astronomy. He just finished his master’s degree at l’Université de Montréal and will be continuing his Ph.D. there.
Galaxy clusters are an exceptional class of object – they are the largest structures in the Universe held together by gravity, and contain hundreds or thousands of individual galaxies, unseen dark matter, and a vast amount of hot gas that gives off X-rays.
In 2015, a team of astronomers led by Tracy Webb at McGill University in Montréal released the first study of SpARCS1049, which was quickly recognized as an exceptional member of this exceptional class. The team’s optical, infrared, and ultraviolet observations of this galaxy cluster revealed a complex structure of clumpy, cool emission regions forming a tail that trails away from the cluster’s central galaxy. As a reminder, galaxy clusters are the largest structures in the Universe held together by gravity. They are made up of three main things: hundreds or thousands of individual galaxies, unseen dark matter, and a vast amount of hot gas that gives off X-rays.
These regions, also known as “tidal tails,” are usually the remnants of a smaller galaxy that has merged with the central galaxy. Studying the near-infrared images revealed a truly surprising fact: the region around the central galaxy was forming stars at a prodigious rate of nearly 900 solar masses per year! (For comparison, our own galaxy -- the Milky Way -- is creating stars at a pedestrian rate of 3 solar masses per year.)
Bending the Bridge Between Two Galaxy Clusters
Abell 2384
Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/SAO/V.Parekh, et al. & ESA/XMM-Newton; Radio: NCRA/GMRT
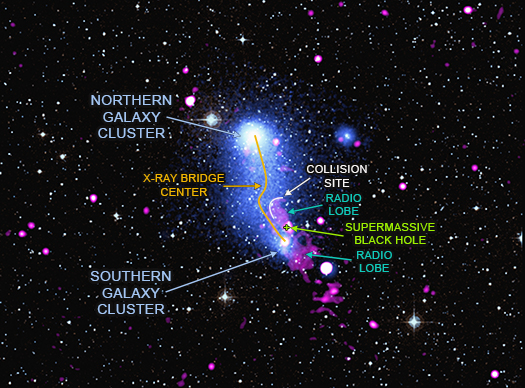
Several hundred million years ago, two galaxy clusters collided and then passed through each other. This mighty event released a flood of hot gas from each galaxy cluster that formed an unusual bridge between the two objects. This bridge is now being pummeled by particles driven away from a supermassive black hole.
Galaxy clusters are the largest objects in the universe held together by gravity. They contain hundreds or thousands of galaxies, vast amounts of multi-million-degree gas that glow in X-rays, and enormous reservoirs of unseen dark matter.