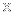Astronomers have discovered a likely explanation for a fracture in a huge cosmic “bone” in the Milky Way galaxy, using NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory and radio telescopes.
The bone appears to have been struck by a fast-moving, rapidly spinning neutron star, or pulsar. Neutron stars are the densest known stars and form from the collapse and explosion of massive stars. They often receive a powerful kick from these explosions, sending them away from the explosion’s location at high speeds.
Enormous structures resembling bones or snakes are found near the center of the galaxy. These elongated formations are seen in radio waves and are threaded by magnetic fields running parallel to them. The radio waves are caused by energized particles spiraling along the magnetic fields.
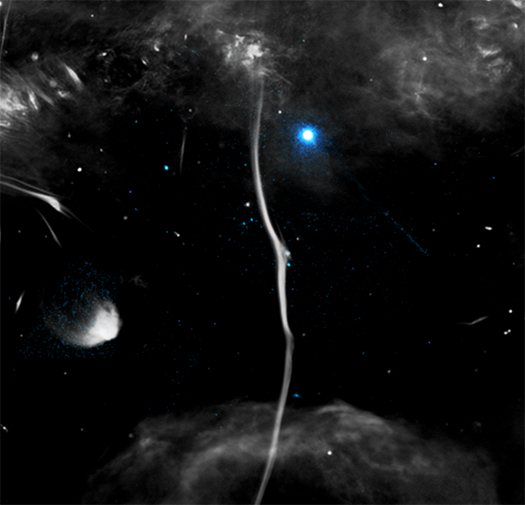

This new image shows one of these cosmic “bones” called G359.13142-0.20005 (G359.13 for short), with X-ray data from Chandra (colored blue) and radio data from the MeerKAT radio array in South Africa (colored gray). Researchers also refer to G359.13 as the Snake.
Examining this image closely reveals the presence of a break, or fracture, in the otherwise continuous length of G359.13 seen in the image. The combined X-ray and radio data provides clues to the cause of this fracture.
Astronomers have now discovered an X-ray and radio source at the location of the fracture, using the data from Chandra and MeerKAT and the National Science Foundation’s Very Large Array. A likely pulsar responsible for these radio and X-ray signals is labeled. A possible extra source of X-rays located near the pulsar may come from electrons and positrons (the anti-matter counterparts to electrons) that have been accelerated to high energies.
The researchers think the pulsar likely caused the fracture by smashing into G359.13 at a speed between one million and two million miles per hour. This collision distorted the magnetic field in the bone, causing the radio signal to also become warped.
At about 230 light-years long, G359.13 is one of the longest and brightest of these structures in the Milky Way. To put this into context, there are more than 800 stars within that distance from Earth. G359.13 is located about 26,000 light-years from Earth, near the center of the Milky Way.
A paper describing these results appeared in the May 2024 issue of the Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society and is available here. The authors of the study are Farhad Yusuf-Zadeh (Northwestern University), Jun-Hui Zhao (Center for Astrophysics | Harvard & Smithsonian), Rick Arendt (University of Maryland, Baltimore County), Mark Wardle (Macquarie University, Australia), Craig Heinke (University of Alberta), Marc Royster (College of the Sequoias, California), Cornelia Lang (University of Iowa), and Joseph Michail (Northwestern).
NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama, manages the Chandra program. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory's Chandra X-ray Center controls science operations from Cambridge, Massachusetts, and flight operations from Burlington, Massachusetts.
This release features two composite images of a long, thin, cosmic structure. With the structure’s vertical orientation, seemingly fragile dimensions, and pale grey color against the blackness of space, the images resemble medical X-rays of a long, thin, bone. The main image shows the structure in its entirety. The inset image is an annotated close-up highlighting an apparent fracture in the bone-like structure.
The structure, called G359.13, or “The Snake”, is a Galactic Center Filament. These filament formations are threaded by parallel magnetic fields, and spiraling, energized particles. The particles cause radio waves, which can be detected by radio arrays, in this case by the MeerKAT array in South Africa.
In the first composite image, the largely straight filament stretches from the top to the bottom of the vertical frame. At each end of the grey filament is a hazy grey cloud. The only color in the image is neon blue, found in a few specks which dot the blackness surrounding the structure. The blue represents X-rays seen by NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory.
In the annotated close-up, one such speck appears to be interacting with the structure itself. This is a fast-moving, rapidly spinning neutron star, otherwise known as a pulsar. Astronomers believe that this pulsar has struck the filament halfway down its length, distorting the magnetic field and radio signal.
In both images, this distortion resembles a small break, or spur, in the bone-like filament.
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||