Supernovas & Supernova Remnants
A Supernova Cocoon Breakthrough
Observations with NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory have provided the first X-ray evidence of a supernova shock wave breaking through a cocoon of gas surrounding the star that exploded. This discovery may help astronomers understand why some supernovas are much more powerful than others.
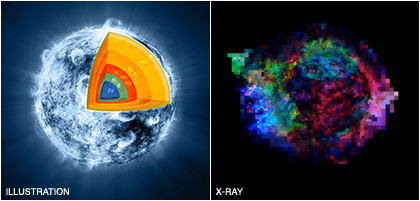
A Star Explodes and Turns Inside Out
A new X-ray study of the remains of an exploded star indicates that the supernova that disrupted the massive star may have turned it inside out in the process. Using very long observations of Cassiopeia A (or Cas A), a team of scientists has mapped the distribution of elements in the supernova remnant in unprecedented detail. This information shows where the different layers of the pre-supernova star are located three hundred years after the explosion, and provides insight into the nature of the supernova.
Remnant of an Explosion With a Powerful Kick?
Vital clues about the devastating ends to the lives of massive stars can be found by studying the aftermath of their explosions. In its more than twelve years of science operations, NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory has studied many of these supernova remnants sprinkled across the Galaxy.
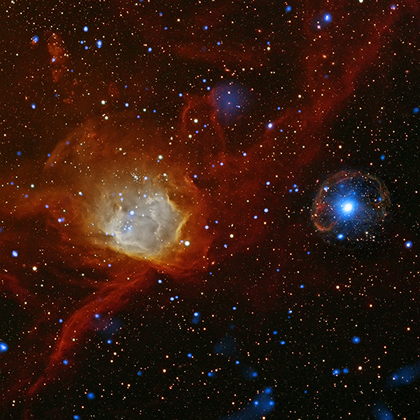
Supernovas on Ice
Sometimes it's hard to get the connection between what happens far away in space and things that you can touch and feel on the ground. Of course, the science of "out there" is intertwined with the science of "right here." A new module for teachers in our Chandra Education section demonstrates that perfectly.

Dr. Gisela Dreschhoff
Since the 1970s, Dr. Gisela Dreschhoff has traveled to Antarctica and Greenland to study the effects from space imprinted on deep ice cores extracted from the ground. While she was initially interested in historic energetic events from the Sun, she has also looked at her data to see if some of the most famous supernova explosions – including Kepler, Tycho, and Cassiopeia A – have also left their mark in the ice.
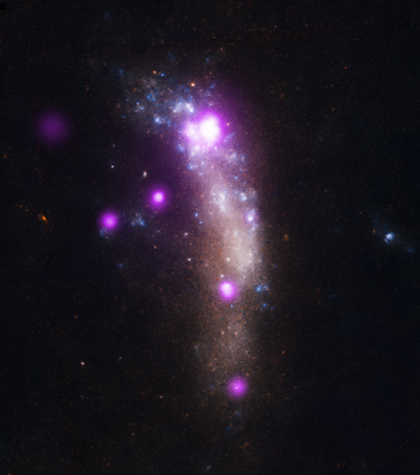
Celestial Bauble Intrigues Astronomers
With the holiday season in full swing, a new image from an assembly of telescopes has revealed an unusual cosmic ornament. Data from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory and ESA's XMM-Newton have been combined to discover a young pulsar in the remains of a supernova located in the Small Magellanic Cloud, or SMC. This would be the first definite time a pulsar, a spinning, ultra-dense star, has been found in a supernova remnant in the SMC, a small satellite galaxy to the Milky Way.
All Eyes on Oldest Recorded Supernova
This image combines data from four different space telescopes to create a multi-wavelength view of all that remains of the oldest documented example of a supernova, called RCW 86. The Chinese witnessed the event in 185 A.D., documenting a mysterious "guest star" that remained in the sky for eight months. X-ray images from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory and the European Space Agency's XMM-Newton Observatory are combined to form the blue and green colors in the image. The X-rays show the interstellar gas that has been heated to millions of degrees by the passage of the shock wave from the supernova.
A Middle-Aged Supernova Remnant
G299.2-2.9 is an intriguing supernova remnant found about 16,000 light years away in the Milky Way galaxy . Evidence points to G299.2-2.9 being the remains of a Type Ia supernova, where a white dwarf has grown sufficiently massive to cause a thermonuclear explosion. Because it is older than most supernova remnants caused by these explosions, at an age of about 4500 years, G299.2-2.9 provides astronomers with an excellent opportunity to study how these objects evolve over time. It also provides a probe of the Type Ia supernova explosion that produced this structure.
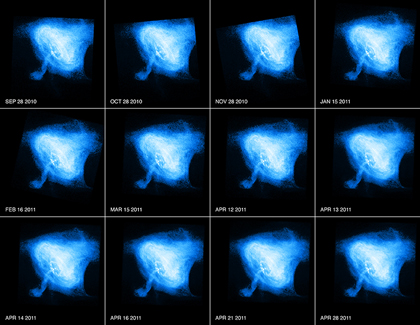
The Crab in Action & The Case of The Dog That Did Not Bark
A new movie from NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory shows a sequence of Chandra images of the Crab Nebula, taken over an interval of seven months. Dramatic variations are seen, including the expansion of a ring of X-ray emission around the pulsar (white dot near center) and changes in the knots within this ring.
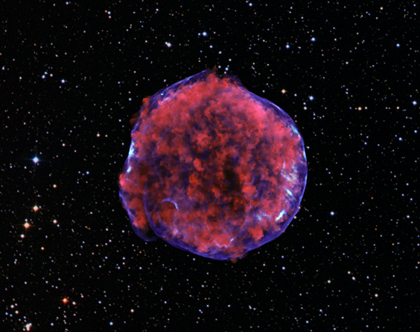
NASA'S Chandra Finds New Evidence on Origin of Supernovas
This Chandra image of the Tycho supernova remnant contains new evidence for what triggered the original supernova explosion. Tycho was formed by a Type Ia supernova, a category of stellar explosion used in measuring astronomical distances because of their reliable brightness. In the lower left region of Tycho is a blue arc of X-ray emission. Several lines of evidence support the conclusion that this arc is due to a shock wave created when a white dwarf exploded and blew material off the surface of a nearby companion star.
Exploding Stars and Stripes
This image comes from a very deep Chandra observation of the Tycho supernova remnant, produced by the explosion of a white dwarf star in our Galaxy. Low-energy X-rays (red) in the image show expanding debris from the supernova explosion and high energy X-rays (blue) show the blast wave, a shell of extremely energetic electrons . These high-energy X-rays show a pattern of X-ray "stripes" never previously seen in a supernova remnant. By rolling the mouse over the color image above, two regions containing stripes in the high energy image can be seen superimposed on the full color version. Some of the brightest stripes can also directly be seen in the full color image, on the right side of the remnant pointing from the outer rim to the interior. The stellar background is from the Digitized Sky Survey and only shows stars outside the remnant.