For Release: December 15, 2025
NASA/MSFC
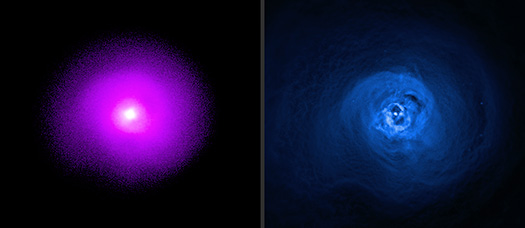
The Perseus Cluster. Left: Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer (IXPE); Right: Chandra X-ray Observatory
Credit: X-ray: (Chandra) NASA/CXC/SAO, (IXPE) NASA/MSFC; Image Processing: NASA/CXC/SAO/N. Wolk and K. Arcand
JPG (864 X 376) | Full Res TIF | Full Res JPG
An international team of astronomers using NASA’s IXPE (Imaging X-ray Polarimetry Explorer) has identified the origin of X-rays in a supermassive black hole’s jet, answering a question that has been unresolved since the earliest days of X-ray astronomy.
IXPE observed the Perseus Cluster, the brightest galaxy cluster in observable in X-rays, for more than 600 hours over a 60-day period between January and March. Not only is this IXPE’s longest observation of a single target to date, it also marks IXPE’s first time observing a galaxy cluster.
Specifically, the team of scientists studied the polarization properties of 3C 84, the massive active galaxy located at the very center of the Perseus Cluster. This active galaxy is a well-known X-ray source and a common target for X-ray astronomers because of its proximity and brightness.
Because the Perseus Cluster is so massive, it hosts an enormous reservoir of X-ray emitting gas as hot as the core of the Sun. The use of multiple X-ray telescopes, particularly the high-resolution imaging power of NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory was essential to disentangle the signals in the IXPE data. Scientists combined these X-ray measurements with data from the agency’s Nuclear Spectroscopic Telescope Array (NuSTAR) mission and Neil Gehrels Swift Observatory.

Chandra & IXPE composite image of the Perseus Cluster.
JPG (864 X 757) | Full Res TIF | Full Res JPG
Credit: X-ray: (Chandra) NASA/CXC/SAO, (IXPE) NASA/MSFC; Image Processing: NASA/CXC/SAO/N. Wolk and K. Arcand
“We’ve already determined that for sources like 3C 84, the X-rays originated from Compton scattering” says Ioannis Liodakis, a Researcher at the Institute of Astrophysics — FORTH in Heraklion, Greece. “With IXPE observations of 3C 84 we had a unique chance to determine the properties of the seed photons.”
The first possible origin scenario for the seed photons is known as synchrotron self-Compton, where lower energy radiation originates from the same jet that produces the highly energetic particles.
In the alternative scenario known as external Compton, seed photons originate from background radiation sources unrelated to the jet.
“The synchrotron self-Compton and external Compton scenarios have very different predictions for their X-ray polarization,” said Frederic Marin, an astrophysicist at the Strasbourg Astronomical Observatory in France. “Any detection of X-ray polarization from 3C 84 almost decisively rules out the possibility of external Compton as the emission mechanism.”
Throughout the 60-day observation campaign, optical and radio telescopes around the world turned their attention to 3C 84 to further test between the two scenarios.
IXPE measured a net polarization of 4% in the X-rays spectrum, with comparable values measured in the optical and radio data. These results strongly favor the synchrotron self-Compton model for the seed photons.
“Separating these two components was essential to this measurement and could not be done by any single X-ray telescope, but by combining the IXPE polarization data with Chandra, NuSTAR, and Swift, we were able to confirm this polarization measurement was associated specifically with 3C 84,” said Sudip Chakraborty, a researcher at the Science and Technology Institute of the Universities Space Research Association in Huntsville, Alabama, near NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center.
While no additional IXPE observations are planned of 3C 84, scientists will continue to analyze data from different locations for different signals.
“While measuring the polarization of 3C 84 was one of the key science goals, we are still searching for additional polarization signals in this galaxy cluster that could be signatures of more exotic physics,” said Steven Ehlert, project scientist for IXPE and astronomer at NASA Marshall.
More about IXPE
IXPE, which continues to provide unprecedented data enabling groundbreaking discoveries about celestial objects across the universe, is a joint NASA and Italian Space Agency mission with partners and science collaborators in 12 countries. IXPE is led by NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center in Huntsville, Alabama. BAE Systems, Inc., headquartered in Falls Church, Virginia, manages spacecraft operations together with the University of Colorado’s Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics in Boulder.
Learn more about IXPE’s ongoing mission here: https://www.nasa.gov/ixpe
Media Contacts:
Megan Watzke
Chandra X-ray Center, Cambridge, Massachusetts
617-496-7998
mwatzke@cfa.harvard.edu
Corinne Beckinger
Marshall Space Flight Center, Huntsville, Alabama
256-544-0034
corinne.m.beckinger@nasa.gov


