CXC Home | Search | Help | Image Use Policy | Latest Images | Privacy | Accessibility | Glossary | Q&A
1
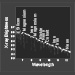
Illustration and Spectrum of Select Elements Detected in GRO J1655-40Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/Technion/N. Keshet et al.; Illustration: NASA/CXC/SAO/M.Weiss
This artist's impression shows the effects of the collapse and supernova explosion of a massive star. A black hole (right) was formed in the collapse and debris from the supernova explosion is raining down onto a companion star (left), polluting its atmosphere.
Astronomers used Chandra to observe the GRO J1655-40 system in 2005 when it was particularly bright in X-rays. Chandra detected signatures of individual elements found in the black hole’s winds by getting detailed spectra — giving X-ray brightness at different wavelengths — embedded in the X-ray light. Some of these elements are highlighted in the spectrum shown here.
Astronomers used Chandra to observe the GRO J1655-40 system in 2005 when it was particularly bright in X-rays. Chandra detected signatures of individual elements found in the black hole’s winds by getting detailed spectra — giving X-ray brightness at different wavelengths — embedded in the X-ray light. Some of these elements are highlighted in the spectrum shown here.
Return to: Finding Clues in the Ruins of an Ancient Dead Star (March 24, 2025)