CXC Home | Search | Help | Image Use Policy | Latest Images | Privacy | Accessibility | Glossary | Q&A
1
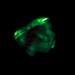
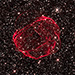
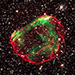
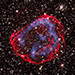
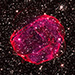
X-ray & Optical Images of SNR 0519-69.0Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/GSFC/B. J. Williams et al.; Optical: NASA/ESA/STScI
Astronomers combined X-ray data from Chandra with those from other telescopes to determine how long ago the star in the supernova remnant called SNR 0519-69.0 exploded and learn about the environment the supernova occurred in. These images show X-ray data from Chandra and Hubble’s optical data of the remnant’s perimeter and surrounding stars. Astronomers concluded that the white dwarf that created this remnant exploded no more than about 670 years ago as seen from Earth.
2
3D Printable Files: SNR 0519-69.0 Tactile Plate (3D Print Credit: NASA/CXC/A. Jubett, using software by Tactile Universe/N. Bonne & C. Krawczyk & Blender)
This tactile plate depicts SNR 0519-69.0, the remnant of a supernova, as a physical relief map based on the intensity of the X-ray data captured by Chandra. The file for this plate can be downloaded and 3D-printed for learners to touch.
On the plate, a mottled blob floats in a dark sky. The blob is the remnant of the supernova, the debris from an exploded white dwarf star. This star exploded several hundred years ago, within Earth's timeframe. Across the surface of the supernova remnant, bulges in the shape are like the lines between the rounded plates on a turtle's shell.
On the plate, a mottled blob floats in a dark sky. The blob is the remnant of the supernova, the debris from an exploded white dwarf star. This star exploded several hundred years ago, within Earth's timeframe. Across the surface of the supernova remnant, bulges in the shape are like the lines between the rounded plates on a turtle's shell.
Return to: Setting the Clock on a Stellar Explosion (September 8, 2022)