CXC Home | Search | Help | Image Use Policy | Latest Images | Privacy | Accessibility | Glossary | Q&A
1
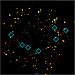
Chandra Deep Field South
The blue boxes on this image pinpoint the seven X-ray sources [supermassive black holes] discovered in the southern field with the Chandra X-ray Observatory that cannot be seen in the Hubble view. These black holes are the most distant ever detected, or the galaxies in which they reside are so dusty that they cannot be seen.
Observation Dates: 1999: Oct 15, Nov 23;
2000: May 27, June 03, Dec 10, 11, 13, 16, 19, 21, 23
Observation Time: 23 days
Instrument: ACIS
Scale: 24 arcmin per side
(Credit: NASA/CXC/R.Giacconi et al. and D.M.Alexander, F.E.Bauer, W.N.Brandt et al.; ID of x-ray sources: A.Koekemoer et al. [2003])
The blue boxes on this image pinpoint the seven X-ray sources [supermassive black holes] discovered in the southern field with the Chandra X-ray Observatory that cannot be seen in the Hubble view. These black holes are the most distant ever detected, or the galaxies in which they reside are so dusty that they cannot be seen.
Observation Dates: 1999: Oct 15, Nov 23;
2000: May 27, June 03, Dec 10, 11, 13, 16, 19, 21, 23
Observation Time: 23 days
Instrument: ACIS
Scale: 24 arcmin per side
(Credit: NASA/CXC/R.Giacconi et al. and D.M.Alexander, F.E.Bauer, W.N.Brandt et al.; ID of x-ray sources: A.Koekemoer et al. [2003])
2
Chandra Deep Field South (no boxes)
Seven X-ray sources [supermassive black holes] were discovered in the southern Deep Field with the Chandra X-ray Observatory that cannot be seen in the Hubble view. These black holes are the most distant ever detected, or the galaxies in which they reside are so dusty that they cannot be seen.
Observation Dates: 1999: Oct 15, Nov 23;
2000: May 27, June 03, Dec 10, 11, 13, 16, 19, 21, 23
Observation Time: 23 days
Instrument: ACIS
Scale: 24 arcmin per side
(Credit: NASA/CXC/R.Giacconi et al. and D.M.Alexander, F.E.Bauer, W.N.Brandt et al.)
Seven X-ray sources [supermassive black holes] were discovered in the southern Deep Field with the Chandra X-ray Observatory that cannot be seen in the Hubble view. These black holes are the most distant ever detected, or the galaxies in which they reside are so dusty that they cannot be seen.
Observation Dates: 1999: Oct 15, Nov 23;
2000: May 27, June 03, Dec 10, 11, 13, 16, 19, 21, 23
Observation Time: 23 days
Instrument: ACIS
Scale: 24 arcmin per side
(Credit: NASA/CXC/R.Giacconi et al. and D.M.Alexander, F.E.Bauer, W.N.Brandt et al.)
3
Hubble Optical Image of Chandra Deep Field South, Close-up
NASA's Hubble Space Telescope reached back to nearly the beginning of time to sample thousands of infant galaxies. This image, taken with Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys, shows several thousand galaxies, many of which appear to be interacting or in the process of forming. Some of these galaxies existed when the cosmos was less than about 2 billion years old. The foreground galaxies, however, are much closer to Earth. Two of them [the white, elongated galaxies, left of center] appear to be colliding.
(Credit: NASA, ESA, the GOODS Team and M. Giavalisco [STScI])
[More Information on the Hubble data]
NASA's Hubble Space Telescope reached back to nearly the beginning of time to sample thousands of infant galaxies. This image, taken with Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys, shows several thousand galaxies, many of which appear to be interacting or in the process of forming. Some of these galaxies existed when the cosmos was less than about 2 billion years old. The foreground galaxies, however, are much closer to Earth. Two of them [the white, elongated galaxies, left of center] appear to be colliding.
(Credit: NASA, ESA, the GOODS Team and M. Giavalisco [STScI])
[More Information on the Hubble data]
4
Hubble Optical Image of Chandra Deep Field South, Full Field
NASA's Hubble Space Telescope reached back to nearly the beginning of time to sample thousands of infant galaxies. This image, taken with Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys, shows several thousand galaxies, many of which appear to be interacting or in the process of forming.
Observation Dates: 5 days, Jul 2002 - Feb 2003
Scale: Approximately 10' x 16'
Instrument: ACS/WFC
(Credit: NASA, ESA, the GOODS Team and M. Giavalisco [STScI])
[More Information on the Hubble data]
NASA's Hubble Space Telescope reached back to nearly the beginning of time to sample thousands of infant galaxies. This image, taken with Hubble's Advanced Camera for Surveys, shows several thousand galaxies, many of which appear to be interacting or in the process of forming.
Observation Dates: 5 days, Jul 2002 - Feb 2003
Scale: Approximately 10' x 16'
Instrument: ACS/WFC
(Credit: NASA, ESA, the GOODS Team and M. Giavalisco [STScI])
[More Information on the Hubble data]
5
Hubble Optical Image of Hubble Deep Field North, Full Field
Because infant galaxies are very faint and very rare, astronomers are using Hubble to search for them over a wide swath of sky. In fact, the new observations cover about 60 times the area of the original Hubble Deep Field Observations, obtained in 1995.
Observation Dates: 5 days, Nov 2002 - May 2003
Scale: Approximately 10' x 16'
Instrument: ACS/WFC
(Credit: NASA, ESA, the GOODS Team and M. Giavalisco [STScI])
[More Information on the Hubble data]
Because infant galaxies are very faint and very rare, astronomers are using Hubble to search for them over a wide swath of sky. In fact, the new observations cover about 60 times the area of the original Hubble Deep Field Observations, obtained in 1995.
Observation Dates: 5 days, Nov 2002 - May 2003
Scale: Approximately 10' x 16'
Instrument: ACS/WFC
(Credit: NASA, ESA, the GOODS Team and M. Giavalisco [STScI])
[More Information on the Hubble data]
6
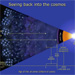
Cosmic Timeline
Observatories continue to reach farther back in time to study the evolution of stars and galaxies. This illustration shows that the Chandra X-ray Observatory and the Hubble Space Telescope's Advanced Camera for Surveys looked back billions of years to see the first galaxies. Their combined effort was part of the Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey (GOODS). Hubble's successor, the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), will gaze even farther back in time to the birth of the first stars.
(Illustration: NASA and Ann Feild [STScI])
Observatories continue to reach farther back in time to study the evolution of stars and galaxies. This illustration shows that the Chandra X-ray Observatory and the Hubble Space Telescope's Advanced Camera for Surveys looked back billions of years to see the first galaxies. Their combined effort was part of the Great Observatories Origins Deep Survey (GOODS). Hubble's successor, the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), will gaze even farther back in time to the birth of the first stars.
(Illustration: NASA and Ann Feild [STScI])
7
Chandra X-ray Image with Scale Bar
Scale bar = 7 arcmin
Credit: NASA/CXC/PSU/D.M.Alexander, F.E.Bauer, W.N.Brandt et al.
Scale bar = 7 arcmin
Credit: NASA/CXC/PSU/D.M.Alexander, F.E.Bauer, W.N.Brandt et al.
Return to GOODS Chandra Deep Fields (19 Jun 03)