NASA's IXPE Helps Researchers Maximize 'Microquasar' Findings

SS 433
Credit: X-ray: (IXPE): NASA/MSFC/IXPE; (Chandra): NASA/CXC/SAO; (XMM): ESA/XMM-Newton; IR: NASA/JPL/Caltech/WISE;
Radio: NRAO/AUI/NSF/VLA/B. Saxton. (IR/Radio image created with data from M. Goss, et al.);
Image Processing/compositing: NASA/CXC/SAO/N. Wolk & K. Arcand
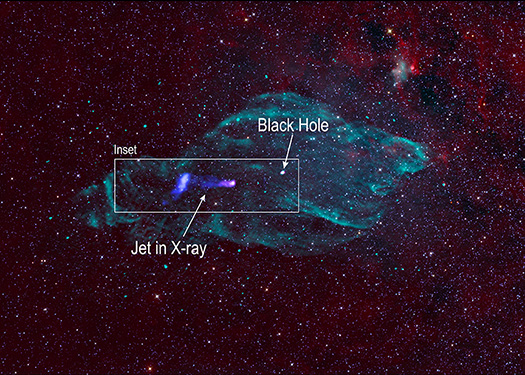
This composite image of the Manatee Nebula captures the jet emanating from SS 433, a black hole pulling material inwards that is embedded in the supernova remnant which spawned it. Radio emission from the supernova remnant are blue-green, whereas the X-ray from IXPE, XMM-Newton and Chandra are highlighted in bright blue-purple and pink-white set against a backdrop of infrared data in red. The black hole emits twin jets of matter traveling in opposite directions at nearly the speed of light.
These jets distort the remnant’s shape into one astronomers dubbed the Manatee. The jets become bright about 100 light-years away from the black hole, where particles are accelerated to very high energies by shocks within the jet. The IXPE data shows that the magnetic field, which plays a key role in how particles are accelerated, is aligned parallel to the jet — aiding our understanding of how astrophysical jets accelerate these particles to high energies.
(Credit: X-ray: (IXPE): NASA/MSFC/IXPE; (Chandra): NASA/CXC/SAO; (XMM): ESA/XMM-Newton; IR: NASA/JPL/Caltech/WISE; Radio: NRAO/AUI/NSF/VLA/B. Saxton. (IR/Radio image created with data from M. Goss, et al.); Image Processing/compositing: NASA/CXC/SAO/N. Wolk & K. Arcand)
A new paper, detailing IXPE’s observations at SS 433, is available in the latest edition of The Astrophysical Journal. IXPE is a collaboration between NASA and the Italian Space Agency with partners and science collaborators in 12 countries. IXPE is led by NASA’s Marshall Space Flight Center. Ball Aerospace, headquartered in Broomfield, Colorado, manages spacecraft operations together with the University of Colorado’s Laboratory for Atmospheric and Space Physics in Boulder.
NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center manages the Chandra program. The Smithsonian Astrophysical Observatory's Chandra X-ray Center controls science operations from Cambridge, Massachusetts, and flight operations from Burlington, Massachusetts.
