Astronomers have discovered one of the most powerful eruptions from a black hole ever recorded in the system known as SDSS J1531+3414 (SDSS J1531 for short). As explained in our press release, this mega-explosion billions of years ago may help explain the formation of a striking pattern of star clusters around two massive galaxies, resembling "beads on a string."
SDSS J1531 is a massive galaxy cluster containing hundreds of individual galaxies and huge reservoirs of hot gas and dark matter. At the center of SDSS J1531, which is located about 3.8 billion light-years away, two of the cluster’s largest galaxies are colliding with each other.
Astronomers used several telescopes to study SDSS J1531 including NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory, and the Low Frequency Array (LOFAR), a radio telescope. This composite image shows SDSS J1531 in X-rays from Chandra (blue and purple) that have been combined with radio data from LOFAR (dark pink) as well as an optical image from the Hubble Space Telescope (appearing as yellow and white). The inset gives a close-in view of the center of SDSS J1531 in optical light, showing the two large galaxies and a set of 19 large clusters of stars, called superclusters, stretching across the middle. The image shows these star clusters are arranged in an ‘S’ formation that resembles beads on a string.
The multiwavelength data provides signs of an ancient, titanic eruption in SDSS J1531, which a team of researchers think was responsible for creation of the 19 star clusters. Their argument is that an extremely powerful jet from the supermassive black holes in the center of one of the large galaxies pushed the surrounding hot gas away from the black hole, creating a gigantic cavity. The evidence for a cavity comes from "wings" of bright X-ray emission, seen with Chandra, tracing dense gas near the center of SDSS J1531. These wings are the edge of the cavity and the less dense gas in between is part of the cavity. LOFAR shows radio waves from the remains of the jet's energetic particles filling in the giant cavity. These features are highlighted in a labeled version of the image.
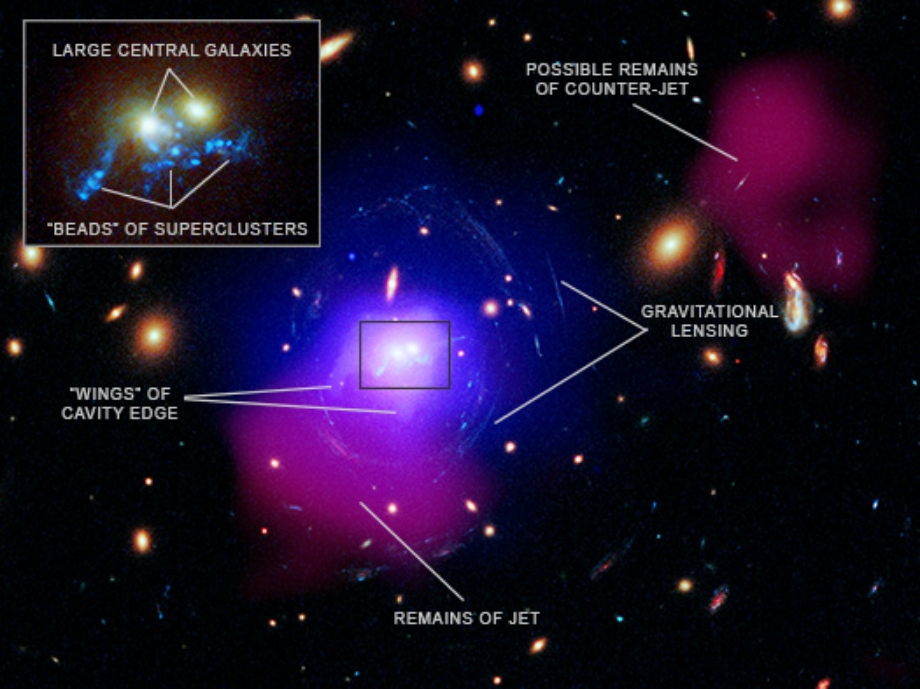 Multiwavelength Image of SDSS J1531, Labeled (Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/SAO/O. Omoruyi et al.; Optical: NASA/ESA/STScI/G. Tremblay et al.; Radio: ASTRON/LOFAR; Image Processing: NASA/CXC/SAO/N. Wolk)
Multiwavelength Image of SDSS J1531, Labeled (Credit: X-ray: NASA/CXC/SAO/O. Omoruyi et al.; Optical: NASA/ESA/STScI/G. Tremblay et al.; Radio: ASTRON/LOFAR; Image Processing: NASA/CXC/SAO/N. Wolk)The astronomers also discovered cold and warm gas located near the opening of the cavity, detected with the Atacama Large Millimeter and submillimeter Array (ALMA) and the Gemini North Telescope, respectively. A separate graphic shows the optical image with the cold gas added in green (left), and the warm gas added in red (right). The team argues that some of the hot gas pushed away from the black hole eventually cooled to form the cold and warm gas shown. The team thinks tidal effects from the two merging galaxies compressed the gas along curved paths, leading to the star clusters forming in the “beads on a string” pattern.






Credit
X-ray: NASA/CXC/SAO/O. Omoruyi et al.; Optical: NASA/ESA/STScI/G. Tremblay et al.; Radio: ASTRON/LOFAR; Image Processing: NASA/CXC/SAO/N. Wolk
Release Date
February 21, 2024
Scale
Image is about 1.5 arcmin (1.4 million light-years) across.
Category
Groups & Clusters of Galaxies, Black Holes
Coordinates (J2000)
RA 15h 31m 10.66s | Dec +34° 14´ 25.71"
Constellation
Corona Borealis
Observation Dates
2 observations Oct 20 and 28, 2015
Observation Time
34 hours (1 day 10 hours)
Obs. ID
17218, 18689
Instrument
ACIS
References
Omoruyi, O. et al., 2024, ApJ, Accepted; arXiv:2312.06762
Color Code
X-ray: blue, purple; Optical: red, green, blue; Radio: dark pink
Red = F2100W + F1130W + F1000W + F770W
Green = F770W + F360M
Blue = F335M + F300M
Distance Estimate
About 3.8 billion light-years (z=0.335)




Featured Images